Arvados integration¶
This section describes the various ways that the benchmark system can work with Arvados Keep and Crunch.
Note
This functionality is experimental.
Note
The commands below assume that the arvados CLI environment and python SDK have been installed and a working environment has been set up. Also, you will need git access
The benefit of the benchmark system is that commands that have been added to the Task Library can be executed on data from Keep or on the local file system and while at the same time allowing execution on a local machine or on a cluster. The system takes care of the mounting/unmounting of data and the job submission and execution.
Running jobs locally¶
To recap, this is how you execute a task with run-task:
benchmark run-task \
--task=metric_filestat \
--input-file=/etc/passwd \
--output-file=test.out \
This will execute a metric task called filestat. On a cluster,
it will submit the task to the cluster, see clustersetup
on how to set it up.
Running a task with data from Keep¶
To run a single task using data in Keep, prefix the
location in the library with the arv= prefix. The following
command will run the metric filestat on the file hs37d5.fa
and output the results in test.out:
benchmark run-task \
--task=metric_filestat \
--input-file=arv=by_id/cce431bdd40f4428666e45bd59c7d41b+6278/hs37d5.fa \
--output-file=test.out \
The same could be achieved by manually mounting Arvados Keep and using the file system path in its mounted location:
mkdir -p /tmp/keep
arv-mount /tmp/keep
benchmark run-task \
--task=metric_filestat \
--input-file=arv=by_id/cce431bdd40f4428666e45bd59c7d41b+6278/hs37d5.fa \
--output-file=test.out \
fusermount -u /tmp/keep
In fact, this is exactly what happens behind the scenes.
run-task is cluster enabled. If a cluster is detected, the job will be submitted to the appropriate queue. See the command line options to run-task on how to control cluster submission.
The command above does not upload the results back to arvados keep. This happens in the next step.
Running a task as an arvados job¶
Running a task through arv-crunch-job will upload the results to Keep while at the same time linking the output to the input and the command executed. This happens when specifying the arvados engine option:
benchmark run-task \
--engine=arvados \
--task=metric_filestat \
--input-file=arv=by_id/cce431bdd40f4428666e45bd59c7d41b+6278/hs37d5.fa \
--output-file=stat.tsv
This will create a job in the arvados system, but run it locally. As before, if the presence of a cluster is detected, the job will be submitted. The UUID of the output and log files generated will be echoed at the end of the script. Through the job, input and output are linked.
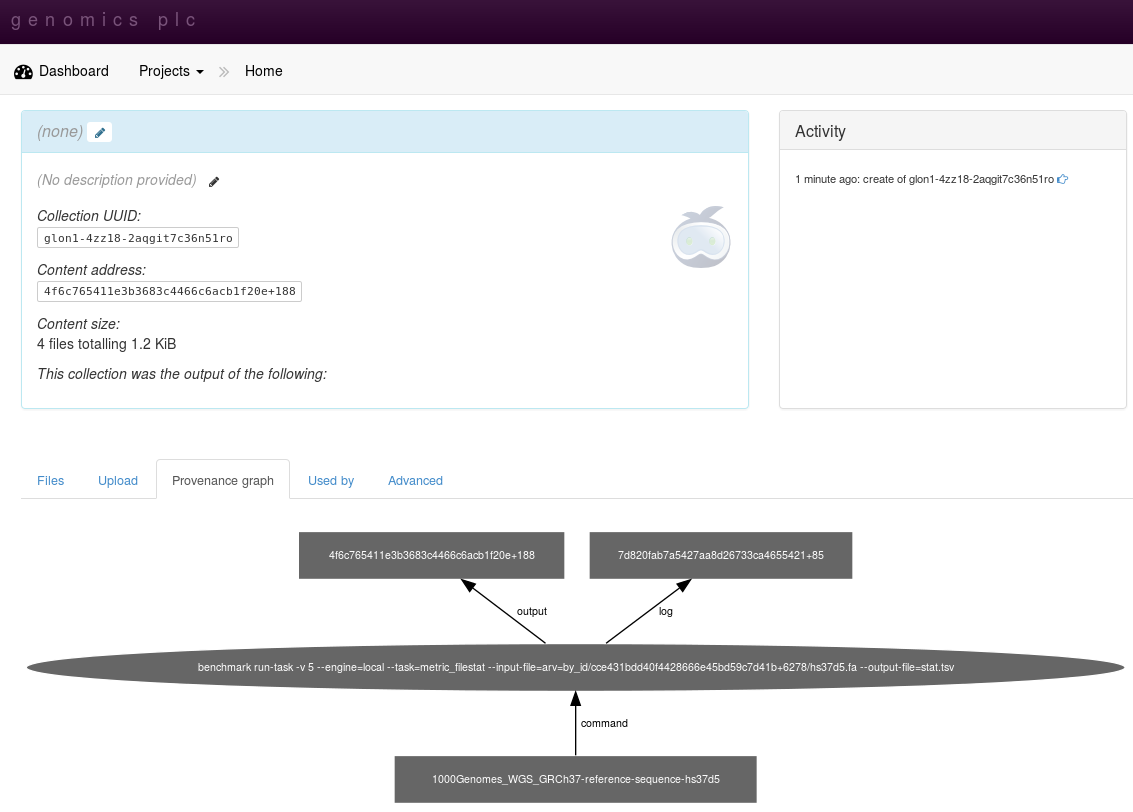
Note
Note that we are referring to the data set by UUID. This is necessary for arvados run-job to identify files within Keep so that it can maintain the link between input and output.
The input files need not come from Keep. This method can also be used to upload data to Keep that has been generated from a local file:
benchmark run-task \
--engine=arvados \
--task=metric_filestat \
--input-file=/etc/passwd \
--output-file=stat.tsv
The provenance graph will link the uploaded file to the command that created it:
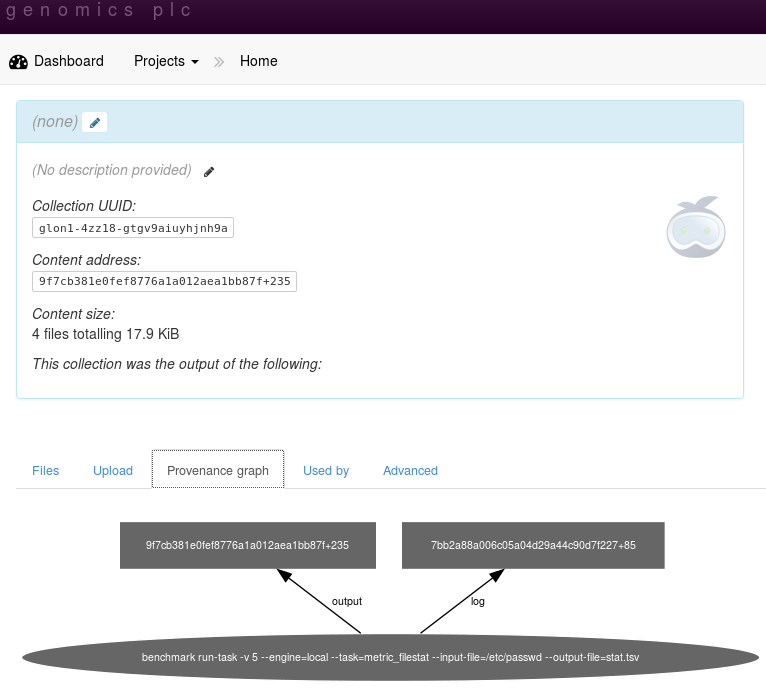
At the moment, the execution uses a locally installed benchmark. As a consequence, the version of the code is not known to Keep. In the future it will be possible to specify a docker image hosted within Keep. This should then permit full provenance tracking that includes the version of code and tools.
Running a workflow with files from Arvados Keep¶
It is possible to run workflows on the local system using the
benchmark workflow system but using files within Keep.
Files that reside within Keep are identified by the
arv= prefix. Save the following in a file called benchmark.yml:
title : >-
Simple Variant-calling + QC workflow
description: >-
A simple workflow calling variants in a set of BAM files
and running bcftools stats for QC.
tags:
- SNV calling
setup:
tools:
- weCall
metrics:
- bcftools_stats
database:
url: sqlite:///./csvdb
input:
reference_fasta: arv=by_id/303fdf14a0443728c5b2e3e0ab25a155+251771/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa
bam: arv=by_id/17322baa637c0b5152c8eef24a6c2b52+2559856/*.bam
regex: ([^/ ,]+).bam
weCall:
options: --numberOfJobs 8 --allowMNPCalls 0 --recalibrateBaseQs 1 --regions=chr1:30000000-31000000
bcftools_stats:
options: --fasta-ref arv=by_id/303fdf14a0443728c5b2e3e0ab25a155+251771/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa --apply-filters
"PASS,."
To run the workflow, type:
benchmark run -v 5 -p 10 make all
This will execute the workflow on the local cluster using data sets stored within Keep.
Note that it is possible to mix both files located on the file system
and files residing in Keep. As before, specifying
--engine=arvados will run the workflow as a crunch script and upload
the data to Keep:
benchmark run --engine=arvados -v 5 -p 10 make all
The dependencies between input and output are stored in Keep:
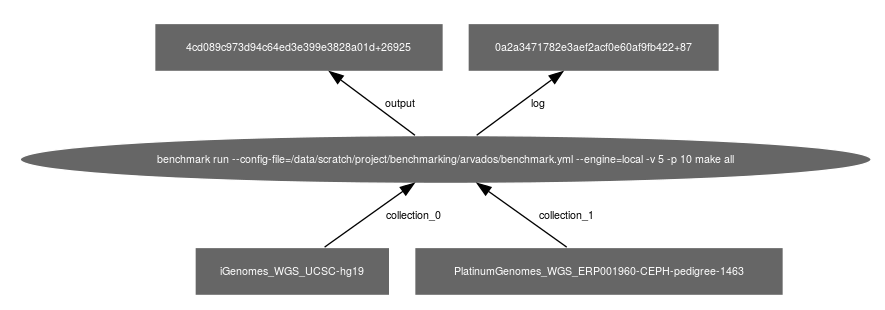
To upload metrics to a database, use the target upload instead
of all:
benchmark run --engine=arvados -v 5 -p 10 make upload
Note
When using an sqlite database, make sure to use an absolute path name as the crunch script will run the benchmark workflow within a temporary local directory.
The UUID of user, job and output will be added to the database into the table arvados_job.
Often a workflow is run and updated iteratively and only the final output should be uploaded to Keep. To do this, it is possible to do:
benchmark run -v 5 -p 10 make all
...
benchmark run --engine=arvados -v 5 -p 10 make keep
The first statemement will run the workflow locally. Once you think all is ok, the second statement will upload the data into Keep without re-running any computations - unless there are files that are out-of-date.
To upload to Keep while simultaneously uploading the metric data to the database, use:
benchmark run -v 5 -p 10 make all
...
benchmark run --engine=arvados -v 5 -p 10 make keep-and-load
This will make sure that the UUID between Keep and the database are synchronized.
Running jobs through Crunch¶
Not implemented yet as crunch not fully installed in London. Should be straight-forward using the CLI interface to daisy.
Notes¶
arv-crunch-job¶
Benchmark tasks can be run using Arvados’ run-command utility.
Create the following script and call it run.job:
{
"script": "run-command",
"script_version": "master",
"repository": "arvados",
"script_parameters": {
"command": [
"benchmark",
"run-task",
"-v 5",
"--task=metric_filestat",
"--input-file=arv=by_id/cce431bdd40f4428666e45bd59c7d41b+6278/hs37d5.fa",
"--output-file=stat.tsv"
]
}
}
Then run this script using the following command:
arv-crunch-job --job="$(cat run.job)"
This happens under the hood when --engine=arvados is set in benchmark run-task.
Todo
- Upload
benchmark.ymlfile when running a workflow. - Implement use of docker image for code and config files from benchmark library.
- Link to collections in Keep within postgres.
- add output_uuid, requires setting the field from CollectionWriter within run-command or querying arvados system after crunch job has finished with job_uuid.
- add collection ids to input files?
- Add meta data/description to new collection created by benchmark jobs: When it was run, by whom, take text from daisy.yml file?
- Run workflows inside Arvados crunch.
- uuid
- Unique identifier for an object in Keep
- Arvados
- The `Arvados Project`_ is dedicated to building a new generation of open source distributed computing software for bioinformatics, data science, and production analysis using massive data sets
- Keep
- Arvados Keep is the data storage of arvados.
- Crunch
- Arvados Crunch is the execution framework of arvados.